|
|
Above: Readers can monitor ozone concentrations for themselves thanks to near-realtime global maps published at NASA's Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer web site. In this map, completed on Sept 6, 2000, the Antarctic ozone hole is prominent as a purple region surrounding the south pole. The column density of ozone, expressed in Dobson Units (DU), above any point on the map is represented by its color. Dark grey denotes low concentrations and red denotes high concentrations. [more information about this image]
Ozone molecules, made up of three atoms of oxygen, comprise a thin layer of the atmosphere that absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. Most atmospheric ozone is found between approximately 9.5 km and 29 km above the Earth's surface. Scientists continuing to investigate this enormous hole are somewhat surprised by its size. The reasons behind the dimensions involve both early-spring conditions in the southern hemisphere, and an extremely intense Antarctic vortex. The Antarctic vortex is an upper-altitude stratospheric air current that sweeps around the Antarctic continent, confining the ozone hole. 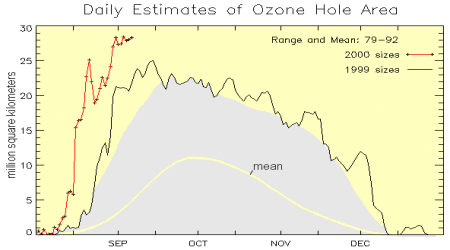
Above: This image from the TOMS web site shows how the size and depth of the 2000 Antarctic ozone hole (red line) compare to 1999's (black line) and with the mean values from 1979 to 1992. The maximum hole size observed in 2000 to date is approximately 28 million square kilometers, while in 1999, the maximum was 25 million square kilometers. The grey shaded region indicates the range of values observed during the interval 1979 to 1992, showing a range from nearly 0 to approx 22 million square kilometers. [more information] "Variations in the size of the ozone hole and of ozone depletion accompanying it from one year to the next are not unexpected," said Dr. Jack Kaye, Office of Earth Sciences Research Director, NASA Headquarters. "At this point we can only wait to see how the ozone hole will evolve in the coming few months and see how the year's hole compares in all respects to those of previous years." "Discoveries like these demonstrate the value of our long-term commitment to providing key observations to the scientific community," said Dr. Ghassem Asrar, Associate Administrator for NASA's Office of Earth Sciences at Headquarters. "We will soon launch QuickTOMS and Aura, two spacecraft that will continue to gather these important data." The measurements released today were obtained using the Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) instrument aboard NASA's Earth Probe (TOMS-EP) satellite. NASA instruments have been measuring Antarctic ozone levels since the early 1970s. Since the discovery of the ozone "hole" in 1985, TOMS has been a key instrument for monitoring ozone levels over the Earth. |